When a tire is inflated and loaded, it deflects. After the load is removed, it returns to original shape. The behavior of the tire without rotating is called "Static Characteristics".
<Vertical deflection>
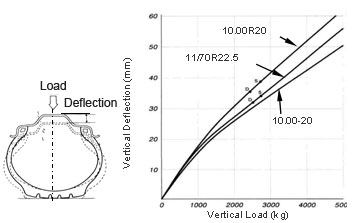
Linear distance between the section height of the unloaded tire and the loaded tire.
|
 |
<Spring rate>
As load increases, so does deflection and as inflation increases, deflection decreases.
Spring rate=Load/Deflection (Kg/mm)
|
<Static Loaded Radius>
When a tire is deflected, the radius is called "Static Loaded Radius". See size designation.
Spring rate is higher in bias tire than in radial, which means radial tire deflects more because of thinner sidewall.
|
When a tire is inflated and loaded, it deflects. After the load is removed, it returns to original shape. The behavior of the tire without rotating is called "Static Characteristics".
<Vertical deflection>
Linear distance between the section height of the unloaded tire and the loaded tire.
|
 |
<Spring rate>
As load increases, so does deflection and as inflation increases, deflection decreases.
Spring rate=Load/Deflection (Kg/mm)
|
<Static Loaded Radius>
When a tire is deflected, the radius is called "Static Loaded Radius". See size designation.
Spring rate is higher in bias tire than in radial, which means radial tire deflects more because of thinner sidewall.
|